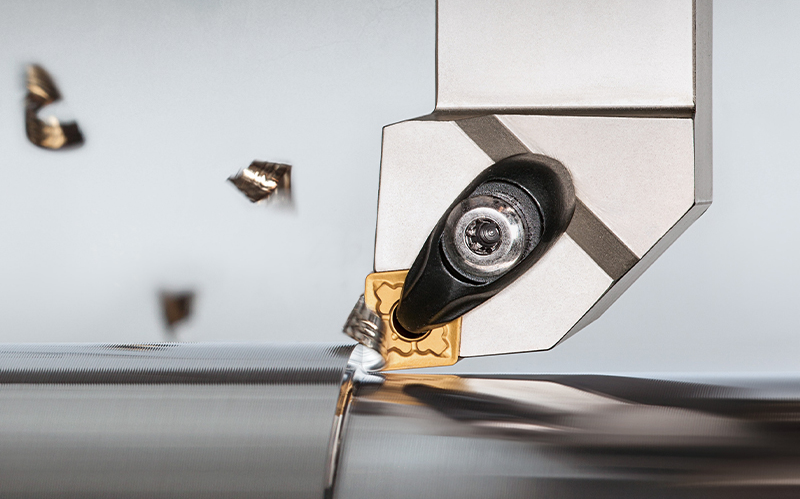
Tool wear is a common problem in mechanical processing, which directly affects processing quality, production efficiency and manufacturing costs. Understanding the causes of tool wear and their solutions can effectively extend the service life of the tool and improve the processing effect. The following are the main causes of tool wear and their corresponding solutions:
To order carbide inserts from us, please contact WhatsApp: +86 13890000254 or email: sales@marsloy.com

1. Main causes of tool wear
1.1 Cutting speed is too high
Reason: Too high cutting speed leads to increased friction and cutting heat between the tool and the workpiece, accelerating tool wear.
Solution: According to the material type and tool characteristics, reasonably reduce the cutting speed to avoid tool wear due to overheating.
1.2 The feed amount is too large
Reason: Excessive feed will increase the cutting force, resulting in increased mechanical stress on the cutting edge of the tool, and the tool is prone to chipping or wear.
Solution: Appropriately reduce the feed amount to ensure smooth cutting process and reduce the load on the tool.
1.3 Cutting depth is too large
Reason: Excessive cutting depth significantly increases the cutting force endured by the tool, resulting in increased tool wear.
Solution: Optimize the cutting depth and adopt a step-by-step cutting method to gradually reach the required depth and reduce the burden on the tool.
1.4 Tool material is not suitable
Reason: Improper selection of tool material cannot meet the hardness, toughness and other requirements of the processing material, resulting in accelerated tool wear.
Solution: Choose appropriate tool materials according to the processing materials, such as carbide, ceramics, diamond coatings, etc., to improve wear resistance and service life.
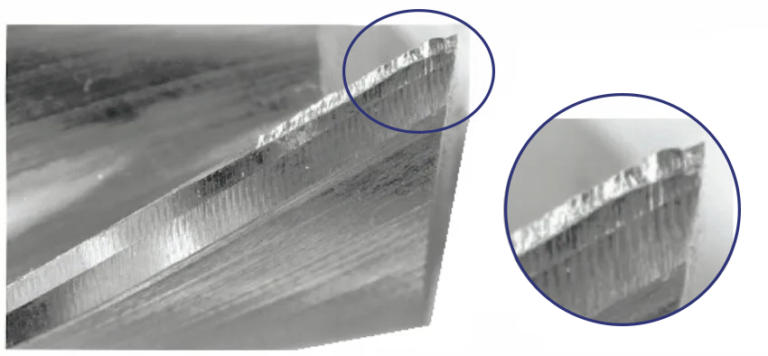
1.5 The geometric angle of the tool is unreasonable
Reason: The rake angle, relief angle, and tool tip angle of the tool are unreasonably set, resulting in increased cutting force or heat accumulation, which intensifies tool wear.
Solution: Optimize the tool geometry angle according to specific processing requirements to ensure reasonable distribution of cutting forces and reduce heat accumulation.
1.6 Insufficient tool cooling
Reason: Insufficient cooling during the cutting process causes the tool temperature to be too high and accelerates tool wear.
Solution: Use enough coolant or lubricant to ensure that the tool is fully cooled during the cutting process.
1.7 Improper selection of cutting fluid
Reason: The type or ratio of cutting fluid is inappropriate, which cannot provide sufficient cooling and lubrication effects and accelerate tool wear.
Solution: Choose the type of cutting fluid suitable for the material and tool being processed, and ensure that the cutting fluid concentration and flow rate are appropriate.
1.8 The hardness of the workpiece material is too high
Reason: The hardness of the workpiece material is higher, causing the tool to bear greater wear force during the cutting process.
Solution: Use tool materials with better wear resistance, or reduce the hardness of the workpiece material through heat treatment and other methods.
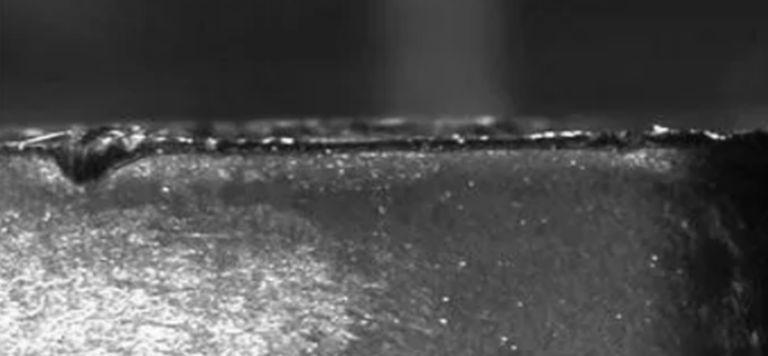
1.9 The tool is not clamped firmly
Reason: The tool is not clamped on the machine tool or is not clamped firmly, causing the tool to fretting during the cutting process and aggravating wear.
Solution: Make sure the tool is securely mounted on the machine tool, using appropriate clamping devices and clamping force.
1.10 Machine tool vibration
Reason: Vibration or instability of the machine tool will cause the tool to receive uneven force during the cutting process and accelerate wear.
Solution: Improve machine tool rigidity, reduce vibration sources, and ensure stable processing.
1.11 Poor chip removal in the cutting area
Reason: Chips accumulate in the cutting area, causing the tool to re-cut the processed chips and increase tool wear.
Solution: Use an effective chip evacuation device or remove chips regularly to ensure a clean cutting area.
1.12 Poor processing environment
Reason: The temperature, humidity or other factors in the processing environment are unstable, which affects the performance and wear of the tool.
Solution: Improve the processing environment, control temperature and humidity, and reduce the negative impact of the environment on the tool.
2. Solution
2.1 Optimize cutting parameters
Reduce cutting speed: According to the characteristics of the processing material and tool, reduce the cutting speed reasonably to reduce heat generation and delay tool wear.
Reduce the feed amount: Reduce the feed amount appropriately to ensure stable cutting force and reduce tool wear.
2.2 Select the appropriate tool material
Select tools according to the workpiece material: such as carbide, ceramic or diamond-coated tools, adapt to materials with different hardness and toughness, and improve the wear resistance of the tools.
2.3 Adjust the tool geometric angle
Optimize the rake angle and relief angle of the tool: adjust the geometric angle of the tool according to the cutting conditions, so that the cutting force and cutting heat are reasonably distributed, and the tool wear is reduced.
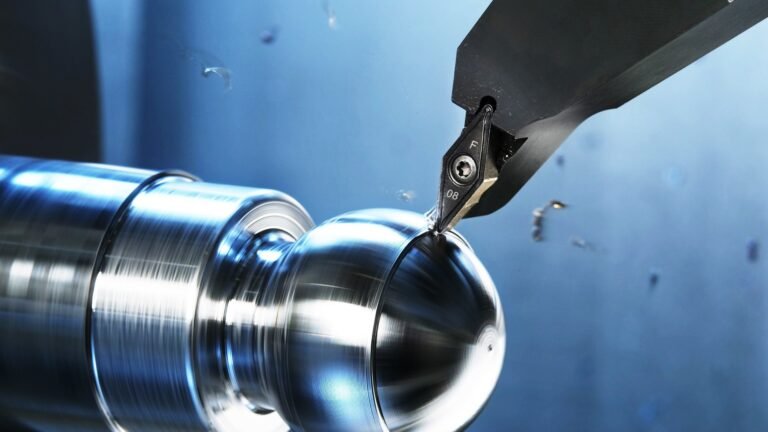

2.4 Improve cooling and lubrication system
Use sufficient coolant: Ensure sufficient coolant supply to reduce the temperature of the cutting zone and reduce thermal wear of the tool.
Choose the right lubricant: Choose the right lubricant according to the cutting material to improve the lubrication effect of the cutting process.
2.5 Regular maintenance and replacement of tools
Regularly check the status of cutting tools: promptly detect tool wear problems and repair or replace them to maintain cutting results.
Replace severely worn tools: When the tool wear reaches a certain level, it should be replaced in time to avoid a decrease in processing quality.
2.6 Improve machine tool and workpiece holding
Make sure the tool is securely mounted: Use high-quality tool holding devices to ensure the stability of the tool on the machine tool.
Improve machine tool rigidity: reduce machine tool vibration, improve the stability of the machining process, and reduce abnormal wear of tools.
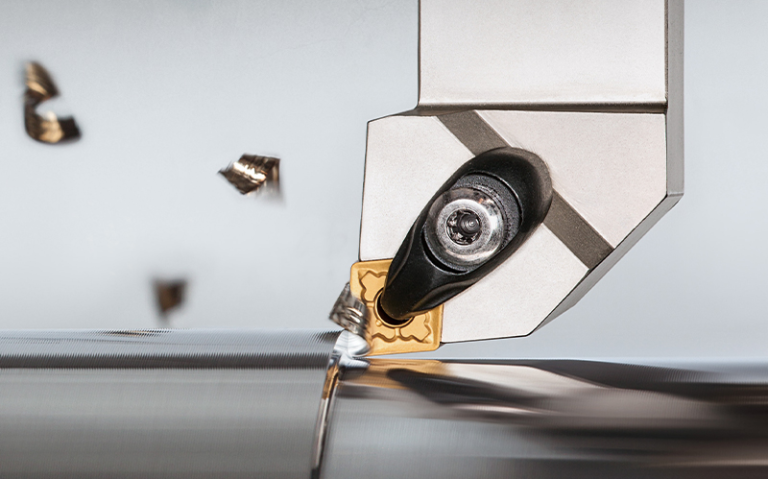

2.7 Use an effective chip removal system
Ensure timely discharge of chips: use an efficient chip discharge system to prevent chips from accumulating in the cutting area and prevent the tool from re-cutting chips.
2.8 Improve the processing environment
Control the temperature and humidity of the processing environment: Reduce the impact of environmental factors on the tool and ensure that the tool works under optimal conditions.



